Apr 12, 2010 microprocessor 80286, 80386, 80486, pentium 80286 microprocessor: Basically this microprocessor is an advanced version of 8086. So before starting with 80286 we must know something abo.
- Comparison Between 8086 80286 80386 80486 And Pentium I5
- Comparison Between 8086 80286 80386 80486 And Pentium Processors
- Comparison Between 8086 80286 80386 80486 And Pentium Cpu
- Comparison Between 8086 80286 80386 80486 And Pentium Processor
- Comparison Between 8086 80286 80386 80486 And Pentium Intel
- The Pentium microprocessor is almost identical to the earlier 80386 and 80486 microprocessors The main difference is that the Pentium has been modified internally to contain a dual cache (instruction and data) and a dual integer unit The Pentium also operates at a higher clock speed of 66 MHz.
- Note: Please make change, 80286 has non-multiplexed Address and Data bus are there.
- (iv) The 80286 microprocessor is an advanced version of the 8086 microprocessor that is designed for multi user and multitasking environments. (iv) The 80386 microprocessor is an enhanced version of the 80286 microprocessor and includes a memory management unit is enhanced to provide memory paging.
- COMPARISON OF PENTIUM PROCESSOR WITH80386 AND 80486 PROCESSOR’S 2. LIMITATIONS OF 80286 THAT LEAD TO 6 has only a 16 bit processor. Maximum segment size of 80286 is 64 KB. 80286 cannot be easily switched between real mode and protected mode because resetting was required. The amount of memory addressable by the 80286 is 16M byte.
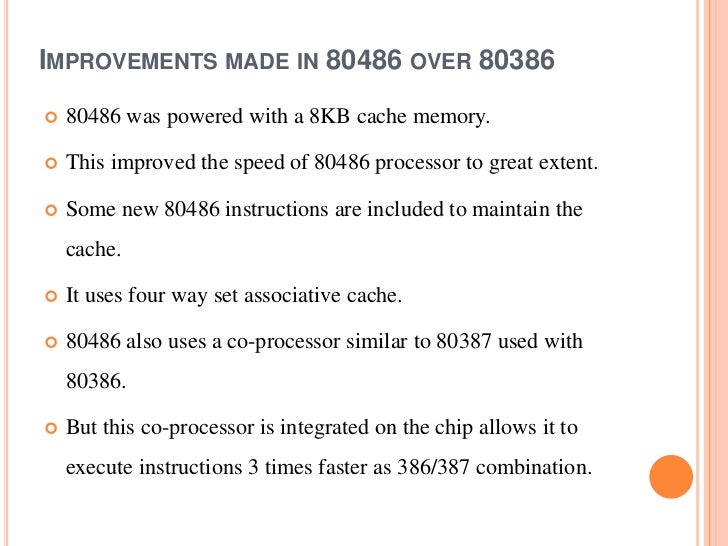
* Tightly coupled pipelining allows the 486 to complete a simple instruction like ALU reg,reg or ALU reg,im every clock cycle. The 386 needed two clock cycles for this.
 * Integrated FPU (disabled or absent in SX models) with a dedicated local bus gives faster floating point calculations compared to the i386+i387 combination.
* Integrated FPU (disabled or absent in SX models) with a dedicated local bus gives faster floating point calculations compared to the i386+i387 combination.
Comparison Between 8086 80286 80386 80486 And Pentium I5
* Improved MMU performance.The 486 has a 32-bit data bus and a 32-bit address bus. This required either four matched 30-pin (8-bit) SIMMs or one 72-pin (32-bit) SIMM on a typical PC motherboard. The 32-bit address bus means that 4 GB of memory can be directly addressed.
Comparison Between 8086 80286 80386 80486 And Pentium Processors
The Intel project manager for the 80486 was Pat Gelsinger.Comparison Between 8086 80286 80386 80486 And Pentium Cpu
Comparison Between 8086 80286 80386 80486 And Pentium Processor
Comparison Between 8086 80286 80386 80486 And Pentium Intel
In May 2006 Intel announced that production of the 80486 would cease at the end of September 2007. Although the chip had long been obsolete for personal computer applications, Intel had continued production for use in embedded systems.